This post is also available in: ![]() English
English ![]() Français (French)
Français (French)
.
– What is the photosynthesis ?
Photosynthesis is a bioenergetic process occurring in chlorophyll cells (located in chloroplasts) when photosynthetic active radiation (PAR) light is present. This process allows a plant to use solar energy converting it into chemical energy. Subsequently, the plant uses this chemical energy to synthesize carbohydrates (assimilates or sugar) using CO2 for the formation of its tissues (Calvin cycle):
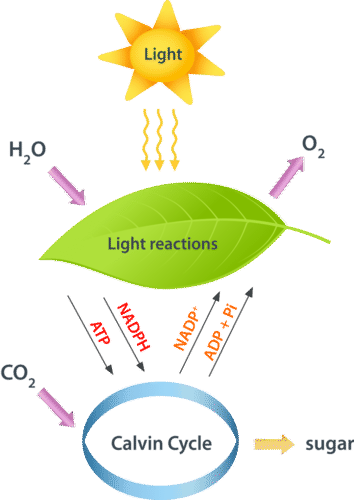
CO2 is an essential gas for the process of photosynthesis. This gas is present quite naturally in the atmosphere in an approximate proportion of 0.038%, or 380 ppm.
.
– What is the role of CO2 ?
In fact, three parameters are necessary for the photosynthesis : water, CO2 and light. The rate of photosynthesis will be determined by the lowest factor of the three. Only by increasing the limiting factor will it be possible to increase the photosynthetic activity of a plant. In the northern hemisphere (in winter conditions) CO2 is often a limiting factor in the greenhouse.
Furthermore, leaf temperature has also an impact on photosynthetic rates. Indeed, photosynthesis is optimal between 15 and 25 ° C. CO2 enters via the stomata located under the leaves :

The air around the leaf (micro-climate) plays an important role on the stomata opening an closing,
Factors favoring the opening of the stomata
- Correct level of humidity and active transpiration
- High atmospheric CO2 concentration (%)
- Good light intensity
- Decrease in the CO2 concentration (%) in the stomatal chamber (pore) brought by an active photosynthesis
Factors favoring stomata closure
- Excessive level of hygrometry and low transpiration
- Increase in the CO2 concentration (%) in the substomatic chamber (pore) brought by an active photorespiration
- Air movement or strong wind which causes the stomata to close to protect the plant against drying out (=stress)
- Insufficient water supply and water stress (roots synthesize acid abscissique which has the property of closing the stomata)
- Extreme temperatures (too hot or too cold)
- Low atmospheric CO2 concentration (%)

Conclusion
Inside a greenhouse the air circulation is necessary to control the humidity and temperature. This also contributes to renewing the concentration of C02 in the air naturally (passive ventilation). The environment in the greenhouse has to allow transpiration while limiting the appearance of fungal diseases (relative humidity % management).
To conclude, equipment helping to bring the CO2 to the stomata will catalyse the photosynthesis rate of the crop. Nowadays, many technologies make it possible to artificially enrich the CO2 concentrations in the greenhouse…
Source:
Carbon Dioxide In Greenhouses: http://www.omafra.gov.on.ca/english/crops/facts/00-077.htm
The Importance of Vertical Air Movement in a Greenhouse:
https://hinova.nl/en/the-importance-of-vertical-air-movement-in-a-greenhouse/#:~:text=Greenhouse%20air%20can%20get%20warmer,reduce%20the%20risk%20of%20wilting.







[…] we have seen in a previous post, the carbon dioxide molecule (or CO2) plays a major role to enhance yields of biological processes, […]